THIS ARTICLE/PRESS RELEASE IS PAID FOR AND PRESENTED BY NINA - Norwegian Institute for Nature Research - read more
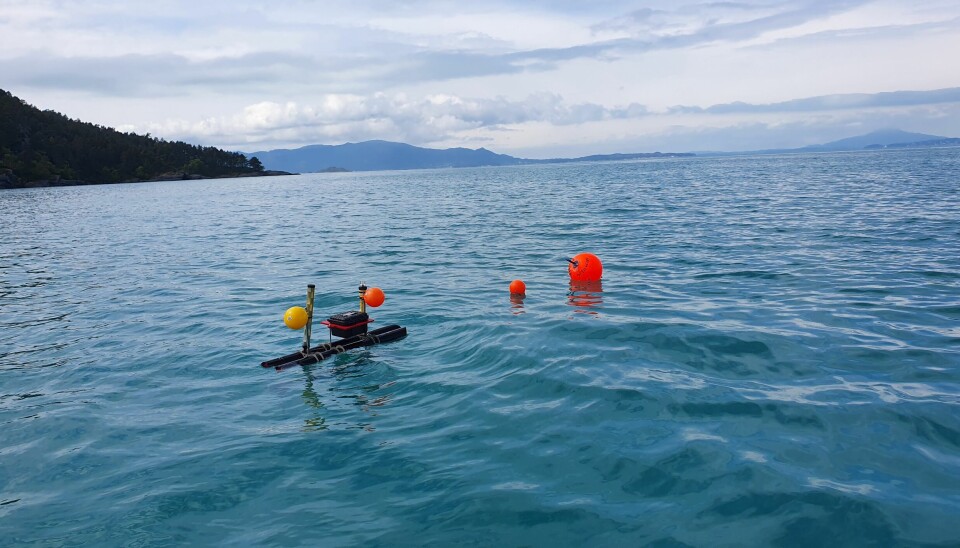

Cost-effective monitoring of salmon lice larvae
Environmental DNA and a new lice trap are teaming up to count salmon lice larvae.
Salmon lice are one of the biggest challenges for today’s Norwegian aquaculture industry and pose a threat to wild salmon. The authorities have therefore introduced several measures to reduce the lice levels in production facilities and the infection pressure on wild fish.
The traffic light system is designed to ensure predictable and sustainable growth in the aquaculture industry. The system uses the infection pressure from salmon lice on wild salmonids as an environmental indicator to determine whether production in an area can increase or must be reduced.
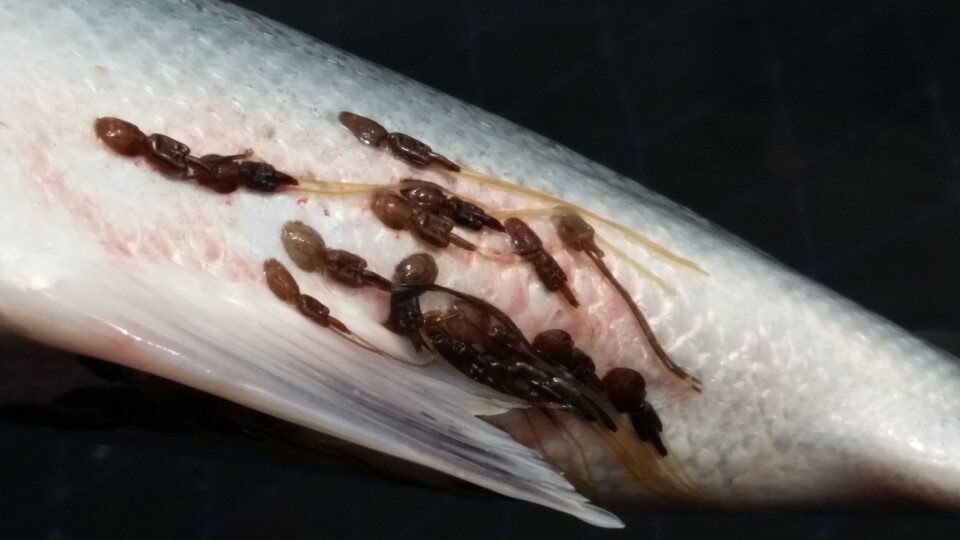
However, monitoring salmon lice is a demanding task. The current management system uses a combination of statistical models that calculate the spread of infectious salmon lice larvae from fish farms and manual counts in the field to monitor the lice on fish.
The field monitoring is done either by catching wild salmon in trawls and purse seines, or by putting farmed salmon into so-called ‘guard cages’ and counting how many lice have infested the fish after two weeks in the ocean.

Lice larvae captured in open sea
Researchers at NINA have collaborated with NTNU to develop a new method for counting salmon lice larvae in the open ocean. This is ground-breaking work that can be scaled up and contribute to cost-effective monitoring of lice larvae along the entire Norwegian coast.

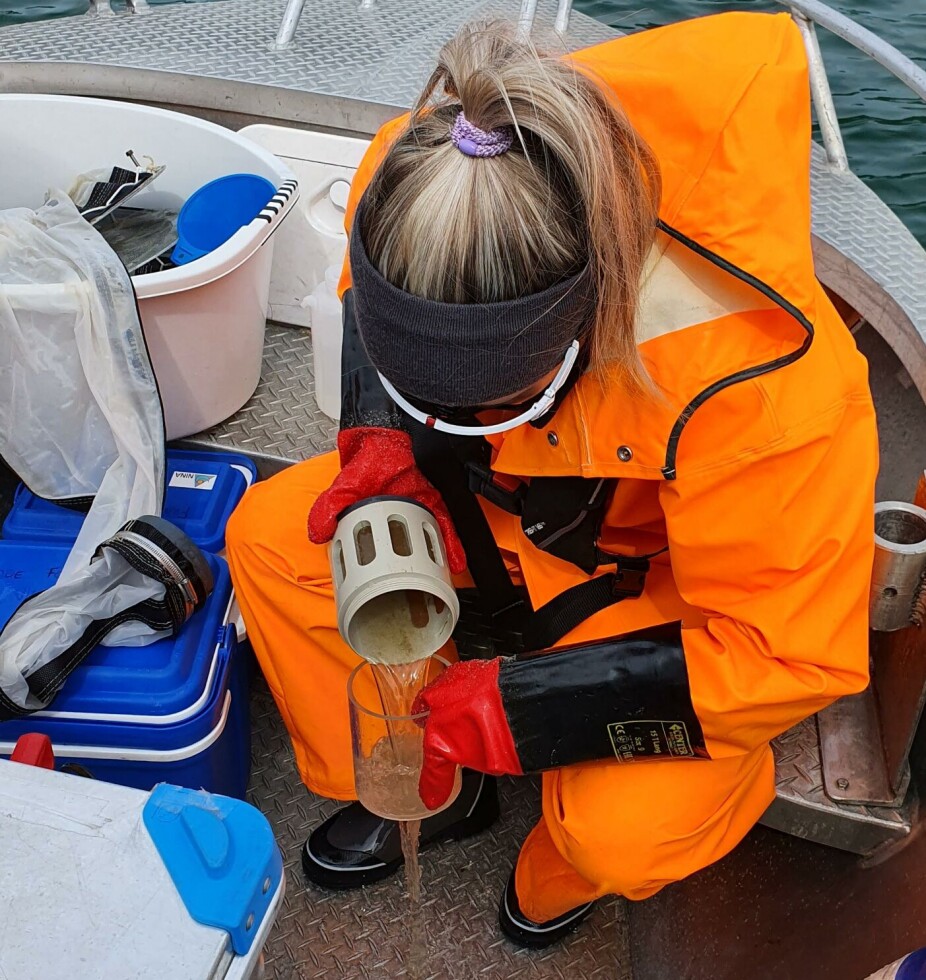
The lice trap filters seawater and collects plankton. The plankton samples are analysed at NINA's genetics lab, where the researchers have developed DNA-based methods for calculating how many salmon lice larvae are present per litre of seawater. Thus, the method can be used to calculate the density of lice larvae in the ocean.

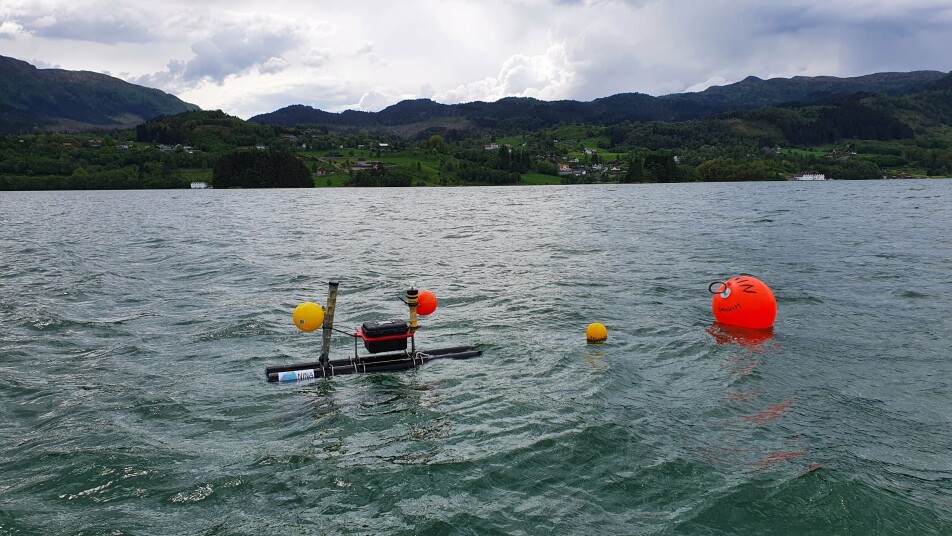
Analyse spread of salmon lice larvae in Hardangerfjord
A total of 12 lice traps have been put out in Etne and Rosendal municipalities in the Hardangerfjord this summer. The Norwegian Institute of Marine Research already has ongoing salmon lice monitoring with guard cages, so the researchers can compare their data with the monitoring results from the Institute of Marine Research. Development of the new method will also help to calibrate the models used in the traffic light system and make the dispersal models even more accurate.
PhD candidate Nathan Mertz and master's students Ingvild Tryggestad and Amanda Andersson at NTNU Sealab have collected large amounts of plankton from various localities in order to analyse the spread of salmon lice in the fjord system.
“These data will be very important and will complement the various national dispersal models for salmon lice developed by the Institute of Marine Research, SINTEF and the Norwegian Veterinary Institute. The method could become an important part of the traffic light system,” says Bengt Finstad, a professor at NTNU Sealab.

This article/press release is paid for and presented by NINA - Norwegian Institute for Nature Research
This content is created by NINA's communication staff, who use this platform to communicate science and share results from research with the public. NINA is one of more than 80 owners of ScienceNorway.no. Read more here.
See more content from NINA:
-
How will climate change affect lakes worldwide?
-
White-tailed sea eagles are breeding in Ireland again after more than a century
-
Could a tunnel help wild reindeer in Norway?
-
Norwegian white-tailed sea eagles are helping to rebuild a lost population in Ireland
-
1 in 4 freshwater species are at risk of extinction: "It's not too late to take action"
-
Insects prefer cold winters with lots of snow




































