This article is produced and financed by University of Oslo - read more
The most popular textbook example of punctuated evolution debunked
Researchers at the University of Oslo have refuted a popular and much-used textbook example about how evolution proceeds during speciation. The example was heavily promoted by the renowned paleontologist Stephen Jay Gould.
Evolutionary biologists have for a long time disagreed on the rate of evolution when new species emerge. Are new species the result of gradual changes – as Charles Darwin suggested – or is evolution speeding up for short periods of time when new species evolve?

World renowned paleontologist Stephen Jay Gould (1941-2002) formulated the theory of punctuated equilibrium together with Niles Eldredge (1943-) in 1972. The theory states that species remain more or less unaltered during their existence with major evolutionary change happening during rapid events of speciation. As evidence for this view, Gould pointed to the fossil record. According to Gould, the fossil record typically show that species do not change significantly after they emerge, and that major changes occurred when new species appeared.
Stephen Jay Gould was one of the twentieth century's most famous evolutionary biologists and a bestselling popular science writer. Some even claimed that Gould was the foremost biologist of his time – perhaps the greatest since Charles Darwin himself – so his words have carried a lot of weight to this day.
In a new paper from researchers at the University of Oslo, the authors claim to have found several methodological problems in the most famous and well-trusted example supporting the theory of punctuated equilibrium.
“We find no evidence for punctuated evolution in our reanalysis of the most recognized dataset that Gould used to support his theory”, says Kjetil Lysne Voje at UiO's Center for Ecological and Evolutionary Synthesis (CEES) at the Department of Biosciences.
Textbook example is rejected
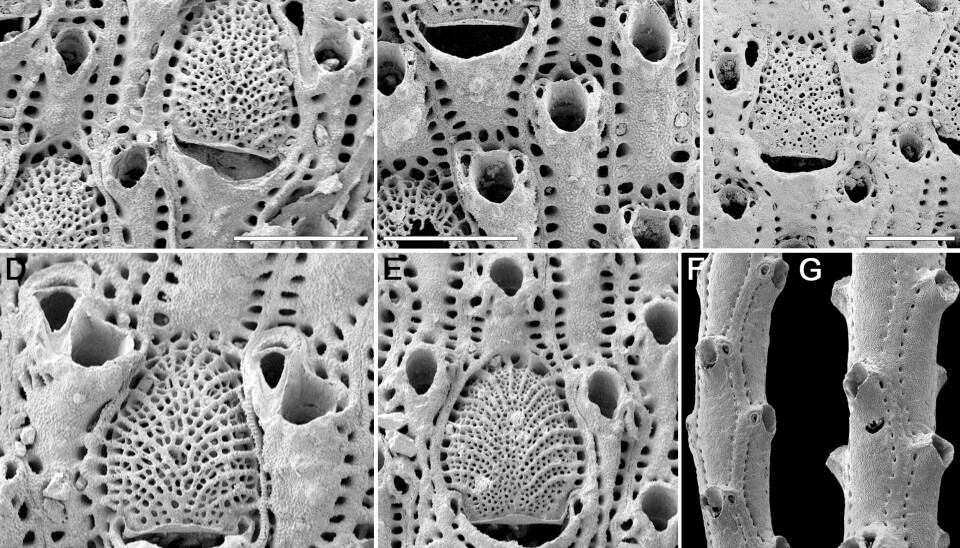
Fossils of the bryozoan genus Metrarabdotos – a group of aquatic invertebrates thoroughly investigated by the excellent paleobiologist Alan Cheetham – have been the prime example of punctuated evolution.
Gould called Metrarabdotos “the most brilliantly persuasive, and most meticulously documented, example ever presented for predominant (in this case, exclusive) punctuated equilibrium in a full lineage” (Gould 2002, page 827).
“We detected some critical methodological issues in the original work on Metrarabdotos. When we take the methodological issues into account, we do not find any evidence of punctuated evolution in our reanalysis of the Metrarabdotos data”, says Kjetil Lysne Voje.
Bryozoans are so small that scientists have to use an electron microscope to study them in detail, but they form colonies that can be quite large (up to 1 meter). Most bryozoans live in the sea, but there are also many species in fresh water. The bryozoan genus Metrarabdotos has been used as a textbook example in evolutionary biology and paleontology, showing how evolution speeds up when new species form compared to a much slower evolution of already established species.
“But our new results show nothing else than a gradual evolution of the bryozoan species both before, during and after the formation of new species”, emphasizes Voje.
Why is this important?
The idea of fast-track evolution during speciation has been controversial. Critics of the theory of punctuated equilibrium found it difficult to believe that the evolutionary processes leading to new species should be markedly different from the processes that cause already existing species to change.
“Species are continuously evolving and our results support the hypothesis that evolution does not "behave" differently when new species emerge”, says Voje.
The paper with the new results was published in the May issue of The American Naturalist. The authors of the study are Kjetil Lysne Voje, Emanuela Di Martino and Arthur Porto.
References:
Kjetil Lysne Voje, Emanuela Di Martino and Arthur Porto: Revisiting a Landmark Study System: No Evidence for a Punctuated Mode of Evolution in Metrarabdotos. The American Naturalist, ahead of print March 17 2020.
Press release from The American Naturalist: The most popular textbook example of punctuated evolution does not hold up to further scrutiny. Published May 2020.


































