An article from Norwegian SciTech News at SINTEF

Taking care of old oil wells
Thousands of old offshore oil wells will have to be plugged to prevent leaks. The process is expensive, but researchers now propose a solution that is much cheaper.
Denne artikkelen er over ti år gammel og kan inneholde utdatert informasjon.
"The first thing we have to do is get an overall picture of the wells in question, their condition, maturity and the cost of the technology", says Kjetil Midthun at SINTEF.
"Then we can generate a database, and after that develop a planning tool designed to reduce costs. The industry and consultancy companies are showing great interest and we have 19 stakeholders participating in this project. The time is right to get the preparatory work started", he says.
Storing up problems for the future
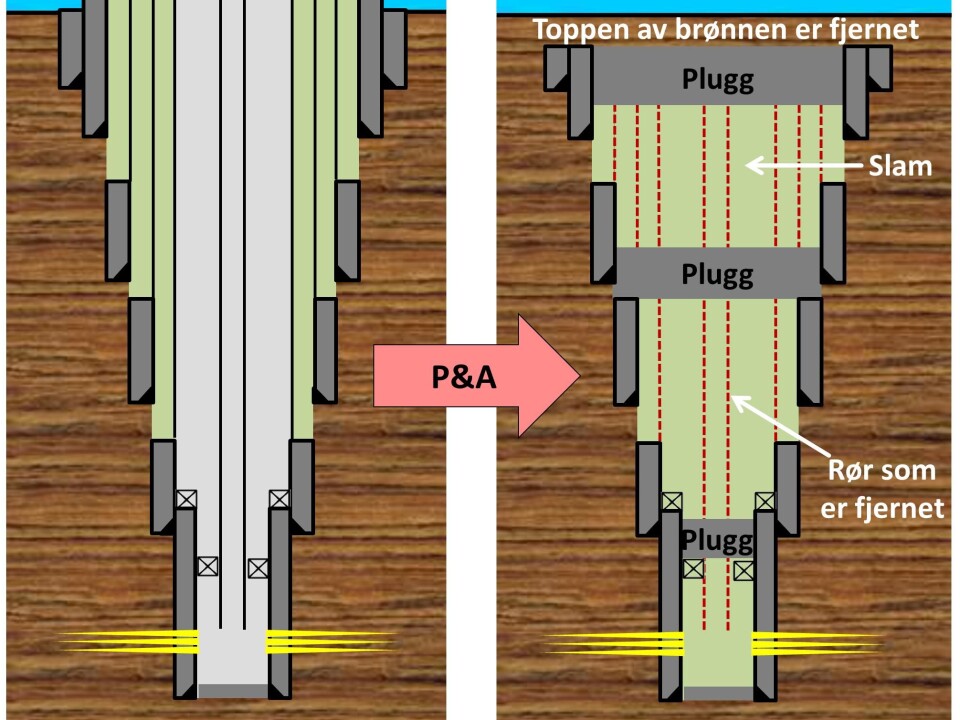
Thousands of oil wells have been drilled on the Norwegian shelf. They can be compared to man-made 'drinking straws' made of cement and steel, each extending for many kilometres below the sea floor. Most of these wells are still in production, but when they are finally abandoned they will have to be plugged to prevent them leaking and causing environmental damage.
In the same way as the Norwegian state takes 78 percent of oil revenues in tax, it must also bear an equally large share of the costs involved in activities such as exploration and the plugging of wells. This means that the state - and the Norwegian taxpayers - will have to bear the greater part of the plugging costs, estimated to be about 100 billion euros.
Both oil companies and researchers have tried to find out how these costs can be reduced, leading to the current launch of a project called ECOPA .
The project is fully funded with 1 million euros from the Research Council of Norway and will combine economic analysis with technological insight. Hopefully it will come up with answers to the following questions: Is it possible to reduce plugging costs? Can the plugging process be simplified and improved? Can plugging be carried out from vessels instead of drilling rigs? What new technologies are required?
Getting the big picture
"Everyone knows that plugging is an immature and very expensive process", says Midthun.
"Our information database is somewhat limited", he says. "Very little detailed information is available about well plugging. For example, when the plugging operation took place, and how. Nor are we aware of factors such as whether or not equipment on the sea floor has been removed, when currently productive wells will be plugged, or what the total costs of the plugging operation will be. For this reason it's important for us to get as big a picture as possible before we proceed", he says.
Many offshore operators and research centres are participating as consultants in this project. The multidisciplinary team of social science and petroleum researchers from SINTEF and NTNU want to establish a close working relationship with both the industry and the authorities. This is because they are in possession of important sources of information. They also share the researchers need for a better overview of the challenges that everyone is facing.
"We also have to review current legislation, regulations and standards", says Midthun. "For example, a secure cement plug on the Norwegian shelf typically has to be 100 metres long, although the standard on the UK shelf is more commonly 30 metres. Such differences result in a variations in plugging costs, and it will be interesting to find out what this will mean in terms of the final bill the Norwegian taxpayer has to pay", he says.
The plugging process
Once the overall picture and information database are in place, the project participants will be able to start developing the planning tool that will be needed to identify bottlenecks in the system. Where will improvements be needed? What plugging technologies will result in the greatest savings?
"Maybe we'll have think out of the box here", says Midthun. "There may be opportunities for savings if plugging campaigns are better planned, if licences work closer together and if their scant and costly resources are better exploited. We aim to use the planning tool to quantify the potential benefits that can be achieved by more plugging campaigns and increasing levels of collaboration", he says.

































